What is Tetragon? 🔍
Tetragon is an exciting open-source observability and security tool developed by Cilium, powered by eBPF (extended Berkeley Packet Filter) technology. It gives you deep visibility into system-level events and network activity within your Kubernetes cluster. With Tetragon, you can trace system calls, monitor command executions in containers, and gain valuable insights for debugging and security auditing.
How Can We Use Tetragon in Kubernetes ? 🐳
Tetragon allows you to monitor the execution of commands within Kubernetes pods by leveraging eBPF (extended Berkeley Packet Filter) technology. This enables you to trace system calls and gather detailed logs of command execution, which can be crucial for debugging and auditing.
Key Features:
- Tracing: Monitor and trace system calls like command executions in real-time.
- Visibility: Gain insights into what’s happening inside your containers and pods.
- Security: Detect and respond to suspicious activities within your cluster.
Demo with Tetragon 🚀
Lets see in action how tetragon works in a kuberentes cluster
Prerequisites
- Vagrant: For creating and managing virtualized development environments.
- VirtualBox: The virtualization software used with Vagrant
Link to the repository for Vagrant Environment: Tetragon-K8s
Custom Vagrant box 🛠️
- We will use custom vagrant box that would install all the necessary tools like
- Minikube
- Helm
- Kubectl
- Docker
- This vagrant box would create separate environment to run a kubernetes cluster and to play around with tetragon.
- This Vagrant environment also consist of anisble playbook that would install cilium and tetragon through helm and also helps in setting up cilium and tetragon
- This playbook would install a demo application on the kubernetes cluster as well
To run the Vagrant box , run this command
vagrant up To access the vagrant box , run this command
vagrant sshTest the Execution Monitoring 🕵️
At the core of Tetragon is the tracking of all executions in a Kubernetes cluster, virtual machines, and bare metal systems. This creates the foundation that allows Tetragon to attribute all system behavior back to a specific binary and its associated metadata (container, Pod, Node, and cluster).
Tetragon exposes the execution events over JSON logs and GRPC stream. The user can then observe all executions in the system.
You can target the Tetragon DaemonSet with a kubectl exec command
kubectl exec -ti -n kube-system ds/tetragon -c tetragon -- tetra getevents -o compact --pods xwingThis command runs tetra getevents -o compact --pods xwing in the single Pod that is a member of the Tetragon DaemonSet. Because there is only a single node in the cluster, it is guaranteed that the “xwing” Pod will also be running on the same node and that Tetragon will be able to capture and report execution events.
The tetra get-events -o compact command returns a compact form of the execution events. To trigger an execution event, you will run a curl command inside the “xwing” Pod/container
Now , open another terminal windows access vagrant box and run this command
kubectl exec -ti xwing -- bash -c 'curl https://ebpf.io/applications/#tetragon'The CLI will print a compact form of the event to the terminal similar to the following output. The example output below is from Kubernetes; the Docker output is very similar.
Now you need to check the output of tetragon deamonset
🚀 process default/xwing /bin/bash -c "curl https://ebpf.io/applications/#tetragon"
🚀 process default/xwing /usr/bin/curl https://ebpf.io/applications/#tetragon
💥 exit default/xwing /usr/bin/curl https://ebpf.io/applications/#tetragon 60The compact execution event contains the event type, the pod name, the binary and the args. The exit event will include the return code; in the case of the curl command above, the return code was 60.
An example output can been seen here
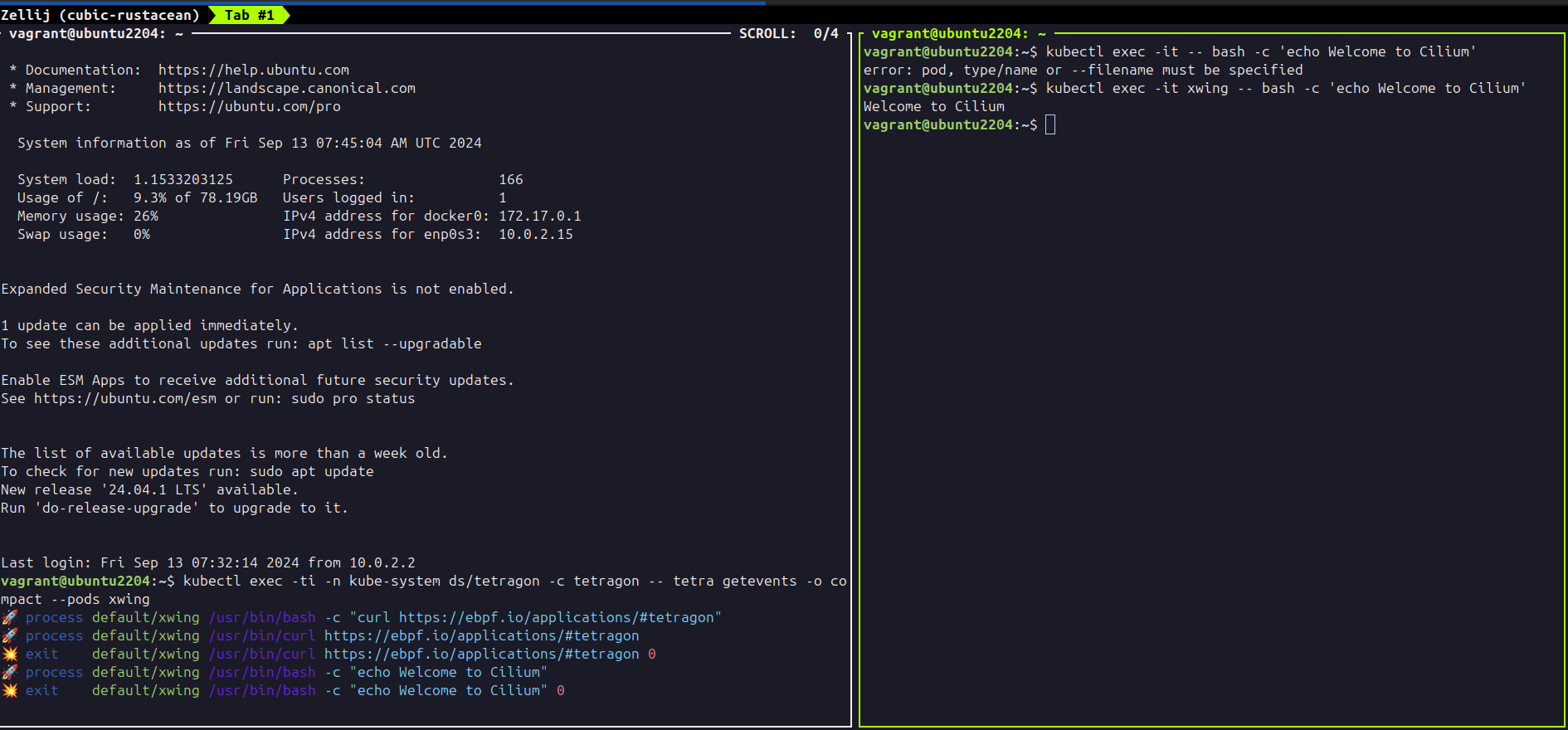
Look for traces of the commands you executed.
Summary
🎯 Tetragon: Dive into the world of eBPF with Tetragon, Cilium’s cutting-edge observability tool.
🏗️ Setup: Spin up a VM environment effortlessly using Vagrant and VirtualBox. Our setup includes Minikube, Docker, kubectl, and Helm—all you need to get started!
📜 Script: We’ve got you covered with a handy script that automates everything from Minikube setup to installing Cilium and Tetragon.
🚀 Testing: Get your hands dirty by deploying a sample app and see Tetragon in action as it tracks command executions within your Kubernetes cluster.
🔍 Recap: We’ve explored how Tetragon can be a game-changer for monitoring command execution in Kubernetes. Dive in and see the magic unfold!
